The Environmental Relative Moldiness Index (ERMI) is an indoor air quality testing method developed by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in collaboration with the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD). ERMI was designed to provide a sensitive and standardized way to assess air quality and mold contamination in homes. This method involves collecting dust samples from various locations within a home, which are then sent to a laboratory for DNA-based analysis to differentiate and quantify specific mold species present in the samples. The laboratory calculates an ERMI score by comparing the concentrations of different mold species in the samples to a national database of mold species concentrations from homes across the U.S.
The ERMI score helps predict the moldiness of a home and assess the potential risk of indoor mold growth and associated health effects. This standardized and objective method provides a comprehensive analysis of mold contamination, allowing homeowners to understand the potential health risks and take appropriate remediation measures.
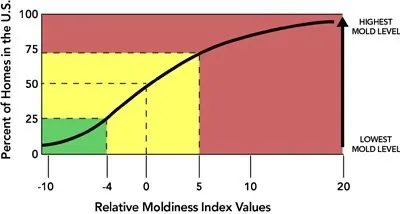
In order to most effectively use this new tool, the ERMI must be compared to a national database. Indices were determined using this method for 1,096 homes across the U.S. as part of the 2006 HUD American Healthy Home Survey. Individual indices, ranked from lowest to highest were used to create a national Relative Moldiness Index (RMI) Scale.
- How Does ERMI Work?
The ERMI test involves the analysis of a single sample of dust from a home. The sample is analyzed using mold-specific quantitative polymerase chain reaction (MSQPCR), a highly specific DNA-based method for quantifying mold species. A simple algorithm is used to calculate a ratio of water damage-related species to common indoor molds and the resulting score is called the Environmental Relative Moldiness Index or ERMI. The ERMI value is typically between -10 and 20.
- How are samples collected for ERMI testing?
ERMI testing depends on settled dust, which behaves as a mold breeding ground. The ERMI sample is a combined sample of dust, typically taken from the living room and master bedroom. The required dust samples can be obtained by vacuuming about 2 square meters each of the bedroom and living room carpet for five minutes each. The outdoor control is integrated into the ERMI sample.
- How can we best utilize ERMI Scores?
During a mold and moisture inspection an ERMI analysis offers data useful to assist in the assessment of the home by a qualified professional. If the ERMI score indicates that there may be water damage in the house, further detailed inspection, including additional testing such as bulk or mold swab testing may reveal a concealed source of water damage and/or mold.
- Does living in an environment with a high ERMI score cause health issues?
There are no explicit guidelines for human health with an ERMI score. The symptoms of mold exposure vary from person to person, depending on the sensitivity of each individual and their degree of mold exposure. The ERMI score should be used in combination with individual mold species quantifications and symptoms of home occupants in order to make a decision. The ERMI score is simply a guideline for the determination of mold exposure levels for home occupants.
Conclusion
ERMI testing definitely has its place if used strategically. ERMI testing can be useful in trying to ascertain the long-term history of a house and an overall sense of the quantity of settled mold spores in the home. ERMI testing is a viable option for defining mold built up by offering comparable information to a baseline from which to start or support a more thorough investigation.
CALL US TODAY to schedule a mold inspection for your home or office in Raleigh, North Carolina. There is never a wrong time to test your property for mold, and it can save you thousands in the future.